使用环境
<!-- 必须 告知插件运行的环境,帮助开发者定位问题 -->
- 操作系统版本:Win10专业版
- 操作系统平台(x86/x64):x64
- VsCode 版本:1.89.1.0
- EIDE 插件版本:3.20.0
- C/C++ 插件版本:1.22.9
- 何种编译器(keil_c51/sdcc/armcc5/armgcc/...):armcc6
- 编译器版本(非编译问题可忽略):非编译问题
描述问题
<!-- 使用简明清晰的语言描述您的问题 -->
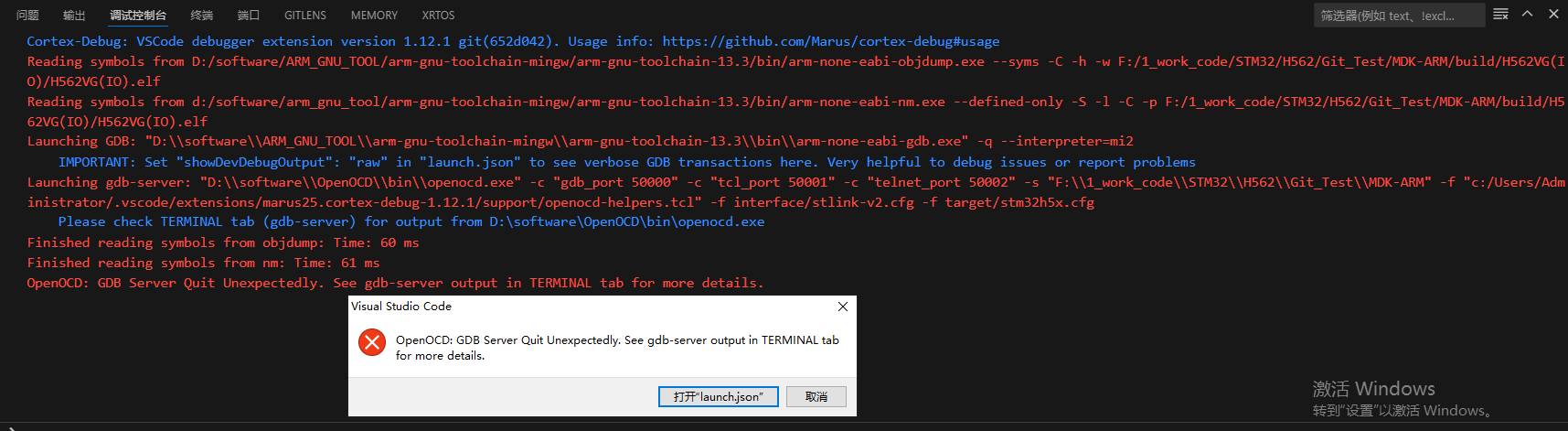
使用芯片为STM32H562VGT6,使用cortex-debug进行debug,采用 openOCD-stlink进行仿真,但是openOCD并未提供H5系列的配置文件,根据H7系列修改而得H5系列配置文件,进行debug时出现如下问题:OpenOCD: GDB Server Quit Unexpectedly. See gdb-server output in TERMINAL tab for more details.
屏幕截图
<!--使用一些截图能够更好地展现问题 -->
1.问题截图如下:
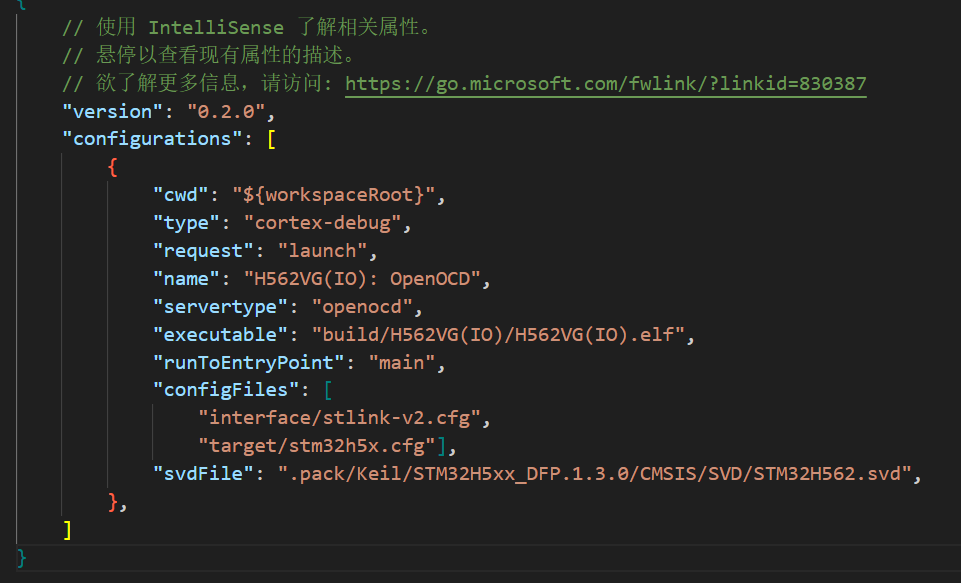
2.lauch.json配置文件:
3.cortex-debug配置(路径有效):
"cortex-debug.armToolchainPath": "D:\software\ARM_GNU_TOOL\arm-gnu-toolchain-mingw\arm-gnu-toolchain-13.3\bin",
"cortex-debug.openocdPath": "D:\software\OpenOCD\bin\openocd.exe",
4.stm32h7x.cfg原文:
#############start
SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-or-later
script for stm32h7x family
#
stm32h7 devices support both JTAG and SWD transports.
#
source [find target/swj-dp.tcl]
source [find mem_helper.tcl]
if { [info exists CHIPNAME] } {
set _CHIPNAME $CHIPNAME
} else {
set _CHIPNAME stm32h7x
}
if { [info exists DUAL_BANK] } {
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK $DUAL_BANK
unset DUAL_BANK
} else {
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK 0
}
if { [info exists DUAL_CORE] } {
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE $DUAL_CORE
unset DUAL_CORE
} else {
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE 0
}
Issue a warning when hla is used, and fallback to single core configuration
if { [set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE] && [using_hla] } {
echo "Warning : hla does not support multicore debugging"
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE 0
}
if { [info exists USE_CTI] } {
set $CHIPNAME.USE_CTI $USE_CTI
unset USE_CTI
} else {
set $CHIPNAME.USE_CTI 0
}
Issue a warning when DUAL_CORE=0 and USE_CTI=1, and fallback to USE_CTI=0
if { ![set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE] && [set $CHIPNAME.USE_CTI] } {
echo "Warning : could not use CTI with a single core device, CTI is disabled"
set $_CHIPNAME.USE_CTI 0
}
set _ENDIAN little
Work-area is a space in RAM used for flash programming
By default use 64kB
if { [info exists WORKAREASIZE] } {
set _WORKAREASIZE $WORKAREASIZE
} else {
set _WORKAREASIZE 0x10000
}
#jtag scan chain
if { [info exists CPUTAPID] } {
set _CPUTAPID $CPUTAPID
} else {
if { [using_jtag] } {
set _CPUTAPID 0x6ba00477
} {
set _CPUTAPID 0x6ba02477
}
}
swj_newdap $CHIPNAME cpu -irlen 4 -ircapture 0x1 -irmask 0xf -expected-id $CPUTAPID
dap create $CHIPNAME.dap -chain-position $CHIPNAME.cpu
if {[using_jtag]} {
jtag newtap $_CHIPNAME bs -irlen 5
}
if {![using_hla]} {
STM32H7 provides an APB-AP at access port 2, which allows the access to
the debug and trace features on the system APB System Debug Bus (APB-D).
target create $CHIPNAME.ap2 mem_ap -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 2
swo create $CHIPNAME.swo -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 2 -baseaddr 0xE00E3000
tpiu create $CHIPNAME.tpiu -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 2 -baseaddr 0xE00F5000
}
target create $CHIPNAME.cpu0 cortex_m -endian $ENDIAN -dap $_CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 0
$CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -work-area-phys 0x20000000 -work-area-size $WORKAREASIZE -work-area-backup 0
flash bank $CHIPNAME.bank1.cpu0 stm32h7x 0x08000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0
if {[set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK]} {
flash bank $CHIPNAME.bank2.cpu0 stm32h7x 0x08100000 0 0 0 $_CHIPNAME.cpu0
}
if {[set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE]} {
target create $CHIPNAME.cpu1 cortex_m -endian $ENDIAN -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 3
$_CHIPNAME.cpu1 configure -work-area-phys 0x38000000 -work-area-size $_WORKAREASIZE -work-area-backup 0
flash bank $_CHIPNAME.bank1.cpu1 stm32h7x 0x08000000 0 0 0 $_CHIPNAME.cpu1
if {[set $_CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK]} {
flash bank $_CHIPNAME.bank2.cpu1 stm32h7x 0x08100000 0 0 0 $_CHIPNAME.cpu1
}
}
Make sure that cpu0 is selected
targets $_CHIPNAME.cpu0
if { [info exists QUADSPI] && $QUADSPI } {
set a [llength [flash list]]
set QSPINAME $CHIPNAME.qspi
flash bank $QSPINAME stmqspi 0x90000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0 0x52005000
} else {
if { [info exists OCTOSPI1] && $OCTOSPI1 } {
set a [llength [flash list]]
set OCTOSPINAME1 $CHIPNAME.octospi1
flash bank $OCTOSPINAME1 stmqspi 0x90000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0 0x52005000
}
if { [info exists OCTOSPI2] && $OCTOSPI2 } {
set b [llength [flash list]]
set OCTOSPINAME2 $CHIPNAME.octospi2
flash bank $OCTOSPINAME2 stmqspi 0x70000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0 0x5200A000
}
}
Clock after reset is HSI at 64 MHz, no need of PLL
adapter speed 1800
adapter srst delay 100
if {[using_jtag]} {
jtag_ntrst_delay 100
}
use hardware reset
#
The STM32H7 does not support connect_assert_srst mode because the AXI is
unavailable while SRST is asserted, and that is used to access the DBGMCU
component at 0x5C001000 in the examine-end event handler.
#
It is possible to access the DBGMCU component at 0xE00E1000 via AP2 instead
of the default AP0, and that works with SRST asserted; however, nonzero AP
usage does not work with HLA, so is not done by default. That change could be
made in a local configuration file if connect_assert_srst mode is needed for
a specific application and a non-HLA adapter is in use.
reset_config srst_nogate
if {![using_hla]} {
if srst is not fitted use SYSRESETREQ to
perform a soft reset
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 cortex_m reset_config sysresetreq
if {[set $_CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE]} {
$_CHIPNAME.cpu1 cortex_m reset_config sysresetreq
}
Set CSW[27], which according to ARM ADI v5 appendix E1.4 maps to AHB signal
HPROT[3], which according to AMBA AHB/ASB/APB specification chapter 3.7.3
makes the data access cacheable. This allows reading and writing data in the
CPU cache from the debugger, which is far more useful than going straight to
RAM when operating on typical variables, and is generally no worse when
operating on special memory locations.
$_CHIPNAME.dap apcsw 0x08000000 0x08000000
}
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -event examine-end {
Enable D3 and D1 DBG clocks
DBGMCU_CR |= D3DBGCKEN | D1DBGCKEN
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00600000 0
# Enable debug during low power modes (uses more power)
# DBGMCU_CR |= DBG_STANDBY | DBG_STOP | DBG_SLEEP D1 Domain
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00000007 0
# DBGMCU_CR |= DBG_STANDBY | DBG_STOP | DBG_SLEEP D2 Domain
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00000038 0
# Stop watchdog counters during halt
# DBGMCU_APB3FZ1 |= WWDG1
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x034 0x00000040 0
# DBGMCU_APB1LFZ1 |= WWDG2
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x03C 0x00000800 0
# DBGMCU_APB4FZ1 |= WDGLSD1 | WDGLSD2
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x054 0x000C0000 0
# Enable clock for tracing
# DBGMCU_CR |= TRACECLKEN
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00100000 0
# RM0399 (id 0x450) M7+M4 with SWO Funnel
# RM0433 (id 0x450) M7 with SWO Funnel
# RM0455 (id 0x480) M7 without SWO Funnel
# RM0468 (id 0x483) M7 without SWO Funnel
# Enable CM7 and CM4 slave ports in SWO trace Funnel
# Works ok also on devices single core and without SWO funnel
# Hack, use stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw with big offset to control SWTF
# SWTF_CTRL |= ENS0 | ENS1
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x3000 0x00000003 0
}
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -event reset-init {
Clock after reset is HSI at 64 MHz, no need of PLL
adapter speed 4000
}
get _CHIPNAME from current target
proc stm32h7x_get_chipname {} {
set t [target current]
set sep [string last "." $t]
if {$sep == -1} {
return $t
}
return [string range $t 0 [expr {$sep - 1}]]
}
if {[set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_CORE]} {
$CHIPNAME.cpu1 configure -event examine-end {
set CHIPNAME [stm32h7x_get_chipname]
global $CHIPNAME.USE_CTI
# Stop watchdog counters during halt
# DBGMCU_APB3FZ2 |= WWDG1
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x038 0x00000040 0
# DBGMCU_APB1LFZ2 |= WWDG2
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x040 0x00000800 0
# DBGMCU_APB4FZ2 |= WDGLSD1 | WDGLSD2
stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x058 0x000C0000 0
if {[set $_CHIPNAME.USE_CTI]} {
stm32h7x_cti_start
}
}
}
like mrw, but with target selection
proc stm32h7x_mrw {used_target reg} {
return [$used_target read_memory $reg 32 1]
}
like mmw, but with target selection
proc stm32h7x_mmw {used_target reg setbits clearbits} {
set old [stm32h7x_mrw $used_target $reg]
set new [expr {($old & ~$clearbits) | $setbits}]
$used_target mww $reg $new
}
mmw for dbgmcu component registers, it accepts the register offset from dbgmcu base
this procedure will use the mem_ap on AP2 whenever possible
proc stm32h7x_dbgmcu_mmw {reg_offset setbits clearbits} {
use $_CHIPNAME.ap2 if possible, and use the proper dbgmcu base address
if {![using_hla]} {
set CHIPNAME [stm32h7x_get_chipname]
set used_target $CHIPNAME.ap2
set reg_addr [expr {0xE00E1000 + $reg_offset}]
} {
set used_target [target current]
set reg_addr [expr {0x5C001000 + $reg_offset}]
}
stm32h7x_mmw $used_target $reg_addr $setbits $clearbits
}
if {[set $_CHIPNAME.USE_CTI]} {
create CTI instances for both cores
cti create $CHIPNAME.cti0 -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 0 -baseaddr 0xE0043000
cti create $CHIPNAME.cti1 -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 3 -baseaddr 0xE0043000
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -event halted { stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart_all }
$_CHIPNAME.cpu1 configure -event halted { stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart_all }
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -event debug-halted { stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart_all }
$_CHIPNAME.cpu1 configure -event debug-halted { stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart_all }
proc stm32h7x_cti_start {} {
set _CHIPNAME [stm32h7x_get_chipname]
# Configure Cores' CTIs to halt each other
# TRIGIN0 (DBGTRIGGER) and TRIGOUT0 (EDBGRQ) at CTM_CHANNEL_0
$_CHIPNAME.cti0 write INEN0 0x1
$_CHIPNAME.cti0 write OUTEN0 0x1
$_CHIPNAME.cti1 write INEN0 0x1
$_CHIPNAME.cti1 write OUTEN0 0x1
# enable CTIs
$_CHIPNAME.cti0 enable on
$_CHIPNAME.cti1 enable on
}
proc stm32h7x_cti_stop {} {
set _CHIPNAME [stm32h7x_get_chipname]
$_CHIPNAME.cti0 enable off
$_CHIPNAME.cti1 enable off
}
proc stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart_all {} {
stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart cti0
stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart cti1
}
proc stm32h7x_cti_prepare_restart {cti} {
set _CHIPNAME [stm32h7x_get_chipname]
# Acknowlodge EDBGRQ at TRIGOUT0
$_CHIPNAME.$cti write INACK 0x01
$_CHIPNAME.$cti write INACK 0x00
}
}
#############end
5.修改得出的H5配置文件(删除了双核、CTI部分的相关配置):
#############start
SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-or-later
script for stm32h5x family
#
stm32h5 devices support both JTAG and SWD transports.
#
source [find target/swj-dp.tcl]
source [find mem_helper.tcl]
if { [info exists CHIPNAME] } {
set _CHIPNAME $CHIPNAME
} else {
set _CHIPNAME stm32h5x
}
if { [info exists DUAL_BANK] } {
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK $DUAL_BANK
unset DUAL_BANK
} else {
set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK 0
}
set _ENDIAN little
Work-area is a space in RAM used for flash programming
By default use 64kB
if { [info exists WORKAREASIZE] } {
set _WORKAREASIZE $WORKAREASIZE
} else {
set _WORKAREASIZE 0x10000
}
#jtag scan chain
if { [info exists CPUTAPID] } {
set _CPUTAPID $CPUTAPID
} else {
if { [using_jtag] } {
set _CPUTAPID 0x6ba00477
} {
set _CPUTAPID 0x6ba02477
}
}
swj_newdap $CHIPNAME cpu -irlen 4 -ircapture 0x1 -irmask 0xf -expected-id $CPUTAPID
dap create $CHIPNAME.dap -chain-position $CHIPNAME.cpu
if {[using_jtag]} {
jtag newtap $_CHIPNAME bs -irlen 5
}
if {![using_hla]} {
STM32H7 provides an APB-AP at access port 2, which allows the access to
the debug and trace features on the system APB System Debug Bus (APB-D).
target create $CHIPNAME.ap2 mem_ap -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 2
swo create $CHIPNAME.swo -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 2 -baseaddr 0xE00E3000
tpiu create $CHIPNAME.tpiu -dap $CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 2 -baseaddr 0xE00F5000
}
target create $CHIPNAME.cpu0 cortex_m -endian $ENDIAN -dap $_CHIPNAME.dap -ap-num 0
$CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -work-area-phys 0x20000000 -work-area-size $WORKAREASIZE -work-area-backup 0
flash bank $CHIPNAME.bank1.cpu0 stm32h5x 0x08000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0
if {[set $CHIPNAME.DUAL_BANK]} {
flash bank $CHIPNAME.bank2.cpu0 stm32h5x 0x08100000 0 0 0 $_CHIPNAME.cpu0
}
Make sure that cpu0 is selected
targets $_CHIPNAME.cpu0
if { [info exists QUADSPI] && $QUADSPI } {
set a [llength [flash list]]
set QSPINAME $CHIPNAME.qspi
flash bank $QSPINAME stmqspi 0x90000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0 0x52005000
} else {
if { [info exists OCTOSPI1] && $OCTOSPI1 } {
set a [llength [flash list]]
set OCTOSPINAME1 $CHIPNAME.octospi1
flash bank $OCTOSPINAME1 stmqspi 0x90000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0 0x52005000
}
if { [info exists OCTOSPI2] && $OCTOSPI2 } {
set b [llength [flash list]]
set OCTOSPINAME2 $CHIPNAME.octospi2
flash bank $OCTOSPINAME2 stmqspi 0x70000000 0 0 0 $CHIPNAME.cpu0 0x5200A000
}
}
Clock after reset is HSI at 64 MHz, no need of PLL
adapter speed 1800
adapter srst delay 100
if {[using_jtag]} {
jtag_ntrst_delay 100
}
use hardware reset
#
The STM32H7 does not support connect_assert_srst mode because the AXI is
unavailable while SRST is asserted, and that is used to access the DBGMCU
component at 0x5C001000 in the examine-end event handler.
#
It is possible to access the DBGMCU component at 0xE00E1000 via AP2 instead
of the default AP0, and that works with SRST asserted; however, nonzero AP
usage does not work with HLA, so is not done by default. That change could be
made in a local configuration file if connect_assert_srst mode is needed for
a specific application and a non-HLA adapter is in use.
reset_config srst_nogate
if {![using_hla]} {
if srst is not fitted use SYSRESETREQ to
perform a soft reset
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 cortex_m reset_config sysresetreq
Set CSW[27], which according to ARM ADI v5 appendix E1.4 maps to AHB signal
HPROT[3], which according to AMBA AHB/ASB/APB specification chapter 3.7.3
makes the data access cacheable. This allows reading and writing data in the
CPU cache from the debugger, which is far more useful than going straight to
RAM when operating on typical variables, and is generally no worse when
operating on special memory locations.
$_CHIPNAME.dap apcsw 0x08000000 0x08000000
}
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -event examine-end {
Enable D3 and D1 DBG clocks
DBGMCU_CR |= D3DBGCKEN | D1DBGCKEN
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00600000 0
# Enable debug during low power modes (uses more power)
# DBGMCU_CR |= DBG_STANDBY | DBG_STOP | DBG_SLEEP D1 Domain
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00000007 0
# DBGMCU_CR |= DBG_STANDBY | DBG_STOP | DBG_SLEEP D2 Domain
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00000038 0
# Stop watchdog counters during halt
# DBGMCU_APB3FZ1 |= WWDG1
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x034 0x00000040 0
# DBGMCU_APB1LFZ1 |= WWDG2
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x03C 0x00000800 0
# DBGMCU_APB4FZ1 |= WDGLSD1 | WDGLSD2
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x054 0x000C0000 0
# Enable clock for tracing
# DBGMCU_CR |= TRACECLKEN
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x004 0x00100000 0
# RM0399 (id 0x450) M7+M4 with SWO Funnel
# RM0433 (id 0x450) M7 with SWO Funnel
# RM0455 (id 0x480) M7 without SWO Funnel
# RM0468 (id 0x483) M7 without SWO Funnel
# Enable CM7 and CM4 slave ports in SWO trace Funnel
# Works ok also on devices single core and without SWO funnel
# Hack, use stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw with big offset to control SWTF
# SWTF_CTRL |= ENS0 | ENS1
stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw 0x3000 0x00000003 0
}
$_CHIPNAME.cpu0 configure -event reset-init {
Clock after reset is HSI at 64 MHz, no need of PLL
adapter speed 4000
}
get _CHIPNAME from current target
proc stm32h5x_get_chipname {} {
set t [target current]
set sep [string last "." $t]
if {$sep == -1} {
return $t
}
return [string range $t 0 [expr {$sep - 1}]]
}
like mrw, but with target selection
proc stm32h5x_mrw {used_target reg} {
return [$used_target read_memory $reg 32 1]
}
like mmw, but with target selection
proc stm32h5x_mmw {used_target reg setbits clearbits} {
set old [stm32h5x_mrw $used_target $reg]
set new [expr {($old & ~$clearbits) | $setbits}]
$used_target mww $reg $new
}
mmw for dbgmcu component registers, it accepts the register offset from dbgmcu base
this procedure will use the mem_ap on AP2 whenever possible
proc stm32h5x_dbgmcu_mmw {reg_offset setbits clearbits} {
use $_CHIPNAME.ap2 if possible, and use the proper dbgmcu base address
if {![using_hla]} {
set CHIPNAME [stm32h5x_get_chipname]
set used_target $CHIPNAME.ap2
set reg_addr [expr {0xE00E1000 + $reg_offset}]
} {
set used_target [target current]
set reg_addr [expr {0x5C001000 + $reg_offset}]
}
stm32h5x_mmw $used_target $reg_addr $setbits $clearbits
}
#############end
期望现象
<!--您期望应该产生的,但实际上却没有发生的结果-->
期望正常进入debug